430. Flatten a Multilevel Doubly Linked List
题目
You are given a doubly linked list, which contains nodes that have a next pointer, a previous pointer, and an additional child pointer. This child pointer may or may not point to a separate doubly linked list, also containing these special nodes. These child lists may have one or more children of their own, and so on, to produce a multilevel data structure as shown in the example below.
Given the head of the first level of the list, flatten the list so that all the nodes appear in a single-level, doubly linked list. Let curr be a node with a child list. The nodes in the child list should appear after curr and before curr.next in the flattened list.
Return the head of the flattened list. The nodes in the list must have all of their child pointers set to null.
Example 1:
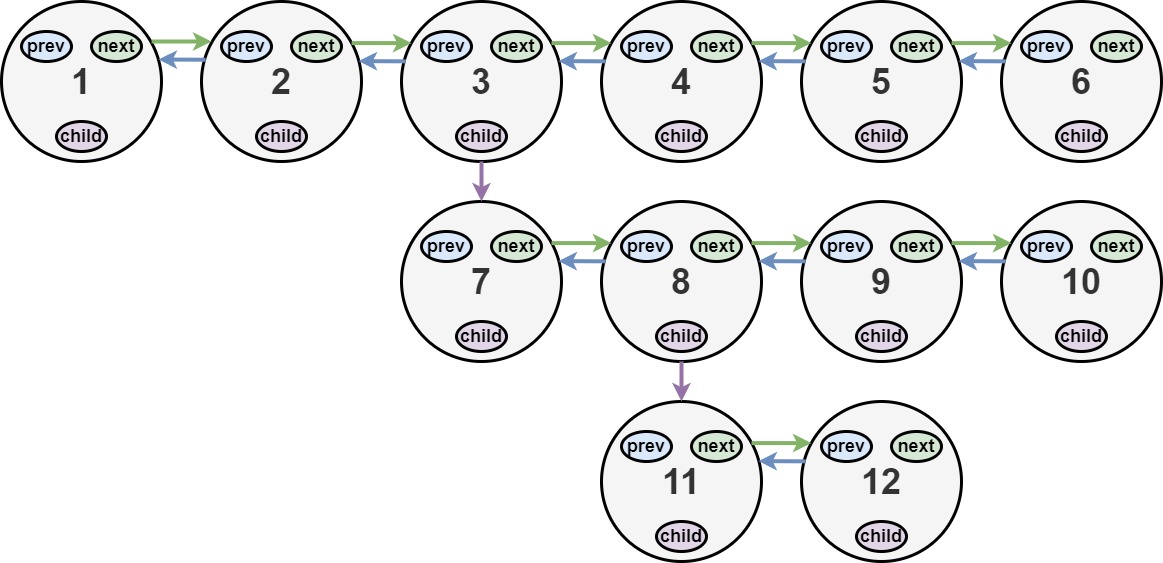
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5,6,null,null,null,7,8,9,10,null,null,11,12] Output: [1,2,3,7,8,11,12,9,10,4,5,6] Explanation: The multilevel linked list in the input is shown. After flattening the multilevel linked list it becomes:
Example 2:

Input: head = [1,2,null,3] Output: [1,3,2] Explanation: The multilevel linked list in the input is shown. After flattening the multilevel linked list it becomes: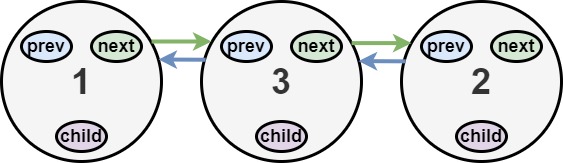
Example 3:
Input: head = [] Output: [] Explanation: There could be empty list in the input.
Constraints:
- The number of Nodes will not exceed
1000. 1 <= Node.val <= 105
How the multilevel linked list is represented in test cases:
We use the multilevel linked list from Example 1 above:
1---2---3---4---5---6--NULL
|
7---8---9---10--NULL
|
11--12--NULLThe serialization of each level is as follows:
[1,2,3,4,5,6,null] [7,8,9,10,null] [11,12,null]
To serialize all levels together, we will add nulls in each level to signify no node connects to the upper node of the previous level. The serialization becomes:
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, null]
|
[null, null, 7, 8, 9, 10, null]
|
[ null, 11, 12, null]
Merging the serialization of each level and removing trailing nulls we obtain:
[1,2,3,4,5,6,null,null,null,7,8,9,10,null,null,11,12]
思路
双向链表的深度优先遍历 双向链表的调试方式记录如下:
def print_doubly_linked_list(head):
node = head
while node:
print(f"Val: {node.val}, Prev: {node.prev.val if node.prev else None}, Next: {node.next.val if node.next else None}, Child: {node.child}")
node = node.next解法
# leetcode submit region begin(Prohibit modification and deletion)
"""
# Definition for a Node.
class Node:
def __init__(self, val, prev, next, child):
self.val = val
self.prev = prev
self.next = next
self.child = child
"""
class Node:
def __init__(self, val, prev, next, child):
self.val = val
self.prev = prev
self.next = next
self.child = child
class Solution:
def flatten(self, head: 'Optional[Node]') -> 'Optional[Node]':
list = []
node = head
while node:
if node.child:
if node.next:
list.append(node.next)
node.next = node.child
node.child.prev = node
node.child = None
if not node.next and list:
child_node = list.pop(-1)
node.next = child_node
child_node.prev = node
node = node.next
return head
# leetcode submit region end(Prohibit modification and deletion)复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度 O(N)
- 空间复杂度 O(N)